Trading is the act of buying and selling any asset to make a profit. The asset can be as diverse as cars, commodities, collectibles, or any financial securities like bonds, stocks, etc. However, we focus on trading from the financial securities perspective. There are different types of trading activities, even from the financial securities perspective.
- Day trading When a trader buys and sells stocks on the same trading day, we refer to it as day trading.
- Swing trading, When a trader buys and sells stocks on the same trading day, we refer to it as swing trading.
- Scalping or Intra-Day trading When a trader buys and sells stocks in a few minutes or seconds, we refer to it as scalping or intra-day trading.
Trading is different from investing in many ways. The difference includes:
- The duration of the positions (trading is short term vs. investing is long term),
- The focus (trading focuses on price movements vs. investing focuses on the underlying business),
- Skills (trading focuses on pattern recognition vs. investing focuses on understanding finance/accounting/strategy/business, etc.)
We outline a few terms you need to understand to trade on this page from Oliver’s playlist here. This is not investment advice. Remember, trading is risky and can potentially lose all or part of your money.
#1 Elephant Bars
Elephant bars are significantly larger bars than the previous bars. Red elephant bars suggest downward price pressure and an indication that smaller red bars are to be expected. Green elephant bars indicate upward price movement and additional smaller green bars to come.
Action tips when you see green elephant bars
Try to get in at the top of a green elephant bar once you have spotted an elephant bar forming. If you miss the green elephant bar, get in on the next bar at a price at or slightly above the top of the green elephant bar. The following bar must be above the previous high.
– Your first buy must be only half of the money you have.
– Also, place a put at the bottom of the green elephant bar. This put is essential to limit your loss if the price moves down. This put allows you to avoid significant losses and stay in business!
– the opposite action is recommended when you spot a red elephant bars
#2 Tails
Tails – Small red or green bar with a long line in one direction is called a tail. There are two types of tails. Tails can be below the bar and or above the bar. The direction of the tail shows the likely future price action. The tails below the bar indicate an upward direction (for both red and green tail bars). And tails above the bar indicate a downward direction (for both red and green tail bars).
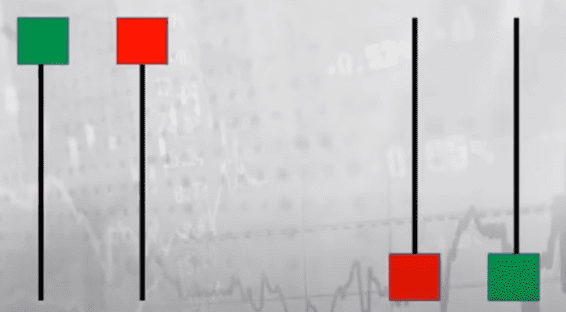
Action tips when you see tails
Get in at the sign of a clear tail.
Also, place a limit at the end of the tail. This is important as it allows you to avoid large losses and stay in business!
The upsides are usually much larger than the losses if you limit them properly.
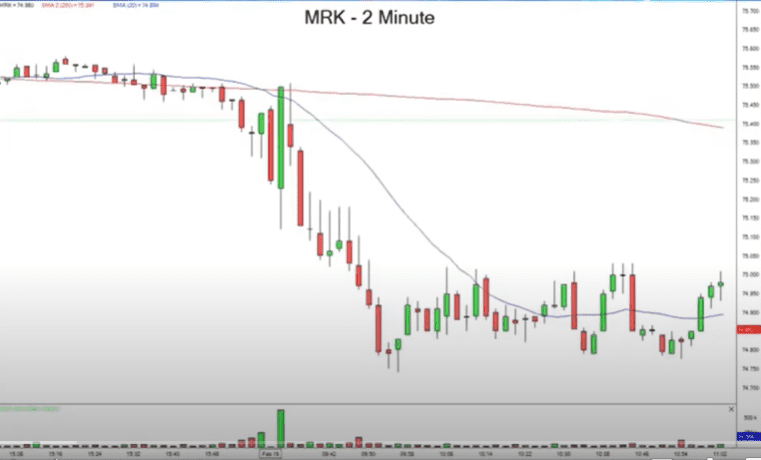
#3 Color Changes
Color changes are when green to red with the red longer on the lower end or red to green with the green longer on the higher end. Remember these two conditions need to be met.
Action tips when you see color changes
- Color changes indicate good times to go in – A green to red color change indicates a shorting opportunity. A red to green color change indicates a long opportunity.
- Remember to go in at the point with the changed color bar gets longer than the previous color bar.
- Limit your losses at the lower of the color that flipped.
BUT remember that this is recommended only when the color change happens near a moving average line.
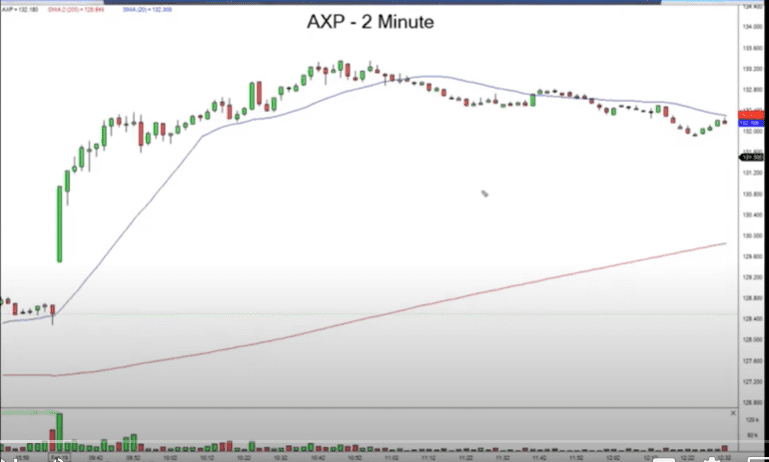
#4 Moving Averages
The moving averages give strong indications and must not be ignored. There are two important conditions you must factor in. The first way the moving average helps is as an indicator of the direction. And the second way the moving average helps is with the timing.
Direction indicator: You have a strong buy signal if the 20 period moving average is above 200 period moving average AND the 20 period moving average is moving upwards. Only then must you look for the buy signals with the strategies outlined above. These include
- Elephant bars
- Color changes
- Tail signals
If the opposite conditions occur, you are looking at a short opportunity.
Timing indicator: You want to enter when you are near the 20 period moving average. You want to exit and take profits when you are away from the 20 period moving average.
#5 Positions
Positive Positions: Positive Positions occur when:
- The 20 period moving average is above 200 periods moving average.
- The 20 periods moving average is increasing
- The stock is above the 20 periods moving average.
Negative Positions: Negative Positions occur when:
- The 20d MA is above 200d MA
- The 20d MA is increasing
- The stock is UNDER the 200d MA
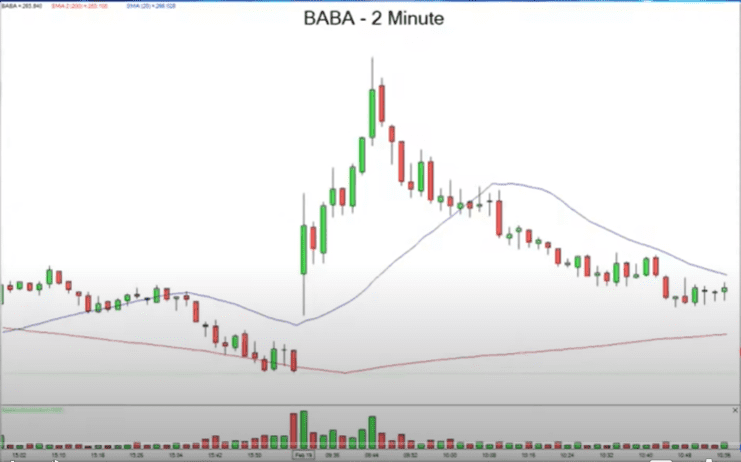
#6 States
- Narrow states: Stocks, 20dMA and 200dMA are close together (relatively)
- Wide states: Stocks, 20dMA and 200dMA are away from each other (relatively)
What you expect the states to do is to swing from the wide state to the narrow state. So you must take positions that benefit from the next move based on the current state. Stock can go up or down from the current position. You must use other indicators to validate your positions.
Some Thoughts on Trading and Reminders
- Keep it simple.
- Most traders lose money. So beware of the risk.
- Your game is not to make money, your game is to prevent losses!
The Truth About Day Trading
Great youtube video on trading by Ben Felix